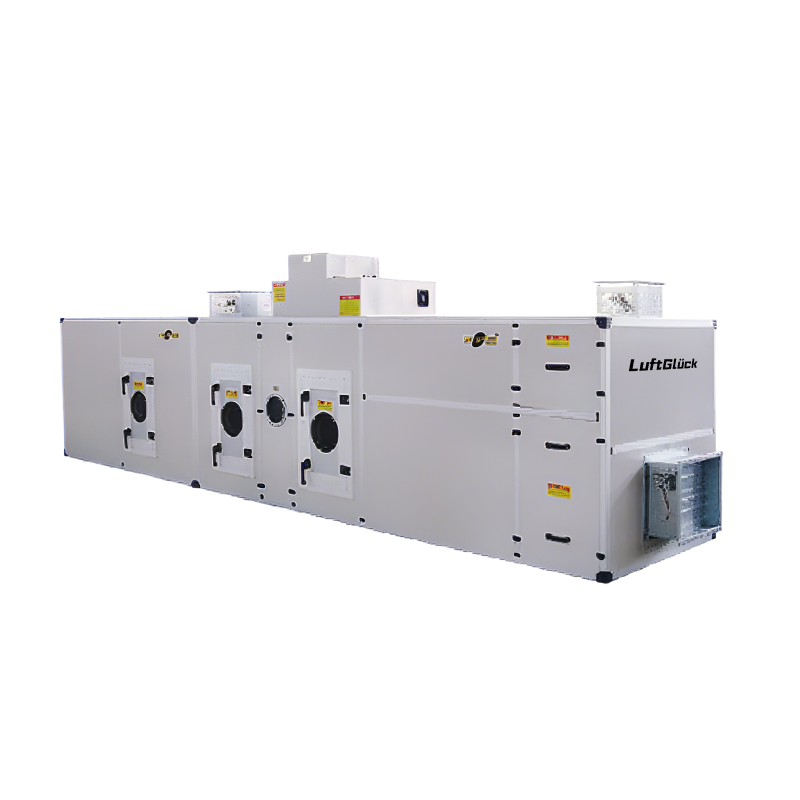
Standard Rotary Dehumidifier-BZLLF Series BZLLF
BZLLF Series – Standard Rotor ModuleThis series features a modular rotor design that requires integration with auxiliary components such as fans, filters, and regeneration systems. It is ideal for flexible system configuration and customized engineering solutions, tailored to specific project requirements.
- Overview
- Recommended Products
Working Principles
The operation of a rotary dehumidifier involves two phases: adsorption and regeneration:
1. Adsorption Process:
Humid air passes through the "treatment sector" (occupying ¾ of the rotor area), where the desiccant material adsorbs moisture, releasing dry air.
2. Regeneration Process:
The rotor rotates into the "regeneration sector" (occupying ¼ of the rotor area). Here, heating (100–140°C) desorbs the moisture, generating high-temperature, high-humidity air that is expelled. The rotor rotates slowly and continuously (8–10 revolutions per hour), enabling cyclic operation.
Application Scope
Rotary dehumidifiers are widely utilized across industries due to their precise humidity control capabilities:
1. Agriculture & Storage
Seed Storage: Maintains low-humidity environments (RH 20%~30%) to prolong seed viability.
Special Crop Drying: Rapid dehydration of high-value crops like Chinese herbal medicines and flowers.
2. Pharmaceuticals & Food
Pharmaceutical Facilities: Ensures stable low humidity (RH 30%~40%) to inhibit microbial growth.
Food Dehydration: Controls humidity during drying processes (e.g., milk powder, tea) to extend shelf life.
3. Special Environments
Sub-Zero Cold Storage: Efficient dehumidification in environments below 0°C to prevent frost buildup.
Labs/Museums: Protects cultural relics or experimental samples from moisture damage.
4. Industrial Manufacturing
Lithium Battery Production: Maintains ultra-dry workshop conditions (dew point below -40°C) to prevent electrode material moisture absorption.
Precision Electronics: Requires ultra-low humidity (RH <10%) for chip or optical lens production to avoid static or oxidation.
Core Advantages
1. High-Efficiency Low-Temperature Dehumidification: Operates stably in sub-zero temperatures (below 0°C) or ultra-low humidity environments (dew point -40°C).
2. Precision Humidity Control: Achieves humidity accuracy within ±1%.
3. Large Airflow Capacity: Ideal for large workshops or high air-exchange scenarios, with single-unit airflow up to tens of thousands of cubic meters per hour.
4. Eco-Friendly & Energy-Efficient: Refrigerant-free design; some models recover regeneration heat to reduce energy consumption.
5. Durability: Rotor lifespan of 5–10 years with low maintenance costs.
Summary
Rotary dehumidifiers, renowned for their low-temperature adaptability, precision humidity control, and industrial-grade reliability, are the preferred choice for demanding humidity-sensitive applications. They excel in sectors like lithium battery production, pharmaceuticals, and precision manufacturing. Despite higher initial costs, their long-term operational efficiency and moisture/mold prevention benefits significantly outperform traditional dehumidification methods.
Standard Rotary Dehumidifier
BZLLF Series

Technical Specifications:
| Parameter | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details |
| Model No. | BZLLF-250D | BZLLF-350D | BZLLF-450D | BZLLF-550D | BZLLF-650D | BZLLF-770D | BZLLF-850D | BZLLF-965D | BZLLF-1050D |
| Dehumidification Capacity | 4 kg/h | 7.2 kg/h | 11.5 kg/h | 17 kg/h | 24.4 kg/h | 34 kg/h | 40 kg/h | 52.2 kg/h | 63.2 kg/h |
| Process Airflow | 500 m³/h | 900 m³/h | 1420 m³/h | 2100 m³/h | 3000 m³/h | 4200 m³/h | 5000 m³/h | 6400 m³/h | 7750 m³/h |
| Regeneration Airflow | 170 m³/h | 300 m³/h | 470 m³/h | 690 m³/h | 990 m³/h | 1390 m³/h | 1650 m³/h | 2110 m³/h | 2560 m³/h |
| Total Installed Power Electric Heating | 6.82 kW | 10.09 kW | 16.44 kW | 25.34 kW | 33.85 kW | 52.7 kW | 64.8 kW | 78.8 kW | 103.3 kW |
| Total Installed Power Steam Heating | - kg/h | - kg/h | - kg/h | 2.84 kg/h | 3.85 kg/h | 6.7 kg/h | 7.8 kg/h | 7.8 kg/h | 17.3 kg/h |
| Regeneration Heating Electric Power | 6 kW | 9 kW | 15 kW | 22.5 kW | 30 kW | 46 kW | 57 kW | 71 kW | 86 kW |
| Regeneration Heating Steam consumption | - kg/h | - kg/h | - kg/h | 40.8 kg/h | 56.1 kg/h | 78.2 kg/h | 96.9 kg/h | 120.7 kg/h | 146.2 kg/h |
| Rotor Drive Power | 0.09 kW | 0.09 kW | 0.09 kW | 0.09 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW |
| Regenerations Fan Power | 0.18 kW | 0.25 kW | 0.25 kW | 0.55 kW | 0.75 kW | 1.1 kW | 2.2 kW | 2.2 kW | 2.2 kW |
| Dehuidification Fan Power | 0.55 kW | 0.75 kW | 1.1 kW | 2.2 kW | 3 kW | 5.5 kW | 5.5 kW | 5.5 kW | 15 kW |
| Dimensions (LxWxH) | 680*620*1310mm | 1010*720*1410mm | 1620*820*1160mm | 1620*920*1260mm | 1920*1020*1360mm | 2020*1120*1360mm | 2020*1220*1440mm | 2220*1320*1660mm | 2320*1420*1780mm |
| Parameter | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details | Details |
| Model No. | BZLLF-1220D | BZLLF-1370D | BZLLF-1525D | BZLLF-1650D | BZLLF-1730D | BZLLF-1800D | BZLLF-1940D | BZLLF-2000D | BZLLF-2200D |
| Dehumidification Capacity | 85.6 kg/h | 107.7 kg/h | 128.9 kg/h | 155.8 kg/h | 171.3 kg/h | 186 kg/h | 217.8 kg/h | 229.2 kg/h | 277.4 kg/h |
| Process Airflow | 10500 m³/h | 13200 m³/h | 15800 m³/h | 19100 m³/h | 21000 m³/h | 22800 m³/h | 26700 m³/h | 28100 m³/h | 34000 m³/h |
| Regeneration Airflow | 3470 m³/h | 4360 m³/h | 5210 m³/h | 6300 m³/h | 6930 m³/h | 7520 m³/h | 8810 m³/h | 9270 m³/h | 11220 m³/h |
| Total Installed Power Electric Heating | 135.1 kW | 165.1 kW | 196.6 kW | 236.6 kW | 260.6 kW | 279.6 kW | 308.6 kW | 323.6 kW | 346.1 kW |
| Total Installed Power Steam Heating | 18.1 kg/h | 18.1 kg/h | 20.6 kg/h | 23.6 kg/h | 25.6 kg/h | 25.6 kg/h | 25.6 kg/h | 25.6 kg/h | 33.1 kg/h |
| Regeneration Heating Electric Power | 117 kW | 147 kW | 176 kW | 213 kW | 235 kW | 254 kW | 283 kW | 298 kW | 313 kW |
| Regeneration Heating Steam consumption | 198.9 kg/h | 249.9 kg/h | 299.2 kg/h | 362.1 kg/h | 399.5 kg/h | 431.8 kg/h | 481.1 kg/h | 506.6 kg/h | 532.1 kg/h |
| Rotor Drive Power | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW | 0.1 kW |
| Regenerations Fan Power | 3 kW | 3 kW | 5.5 kW | 5.5 kW | 7.5 kW | 7.5 kW | 7.5 kW | 7.5 kW | 15 kW |
| Dehuidification Fan Power | 15 kW | 15 kW | 15 kW | 18 kW | 18 kW | 18 kW | 18 kW | 18 kW | 18 kW |
| Dimensions (LxWxH) | 2420*1620*1680mm | 2620*1720*1880mm | 2720*1920*1980mm | 2820*2120*2080mm | 2920*2120*2180mm | 3020*2220*2280mm | 3120*2320*2380mm | 3220*2320*2480mm | 3320*2620*2680mm |
* Product specifications may be modified without notice to improve performance.
Note:
1. The desiccant wheel thickness is 200 mm, with a standard regeneration temperature of 140°C.
2. The rated dehumidification capacity refers to the theoretical value under the rated airflow range, measured when the inlet air temperature is 27°C and relative humidity is 60%.
3. "D" indicates electric heating as the regeneration method, while "Q" indicates steam heating, with a steam gaugepressure of 4.5±0.5 kgf/cm².
1. Structure and Level of Integration
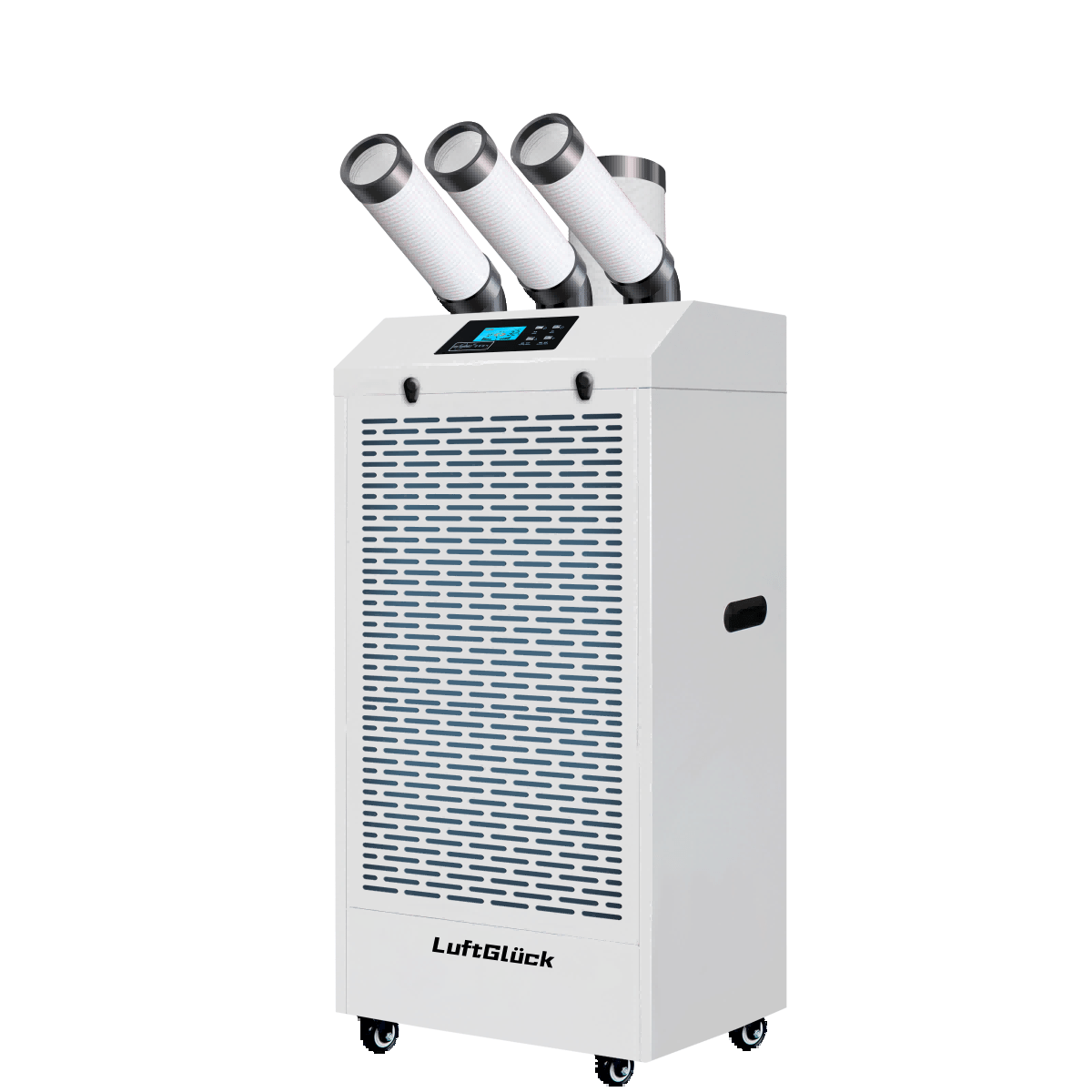
Single-unit Rotary Dehumidier |
Standard Rotary Dehumidifier |
Integrated Design: Combines the fan, rotor, regeneration heating system, and control system into a single cabinet-style unit, similar to a residential air conditioner's "cabinet-type" form. |
Split-Type or Modular Design: Typically consists of separate components, including a processing unit (housing the rotor) and a regeneration unit (with heater), and may require external ductwork and control systems for enhanced flexibility. |
Compact Size: Ideal for space-constrained environments. |
Larger Footprint: Requires dedicated installation space or a separate mechanical room. |
2. Application Scenarios
Single-unit Rotary Dehumidier |
Standard Rotary Dehumidifier |
Small to Medium Spaces: Examples include laboratories, small warehouses, cleanrooms, precision instrument rooms, etc. |
Large-Scale Industrial Applications: Designed for lithium battery factories, pharmaceutical facilities, food drying lines, etc., handling high airflow volumes (tens of thousands of m³/h) and ultra-low humidity (dew point below -40°C). |
Mobility Requirements: Can be placed directly on the floor without complex installation, ideal for temporary or decentralized dehumidification needs. |
Fixed Installation: Requires integration with ductwork and moisture exhaust systems, suitable for long-term stable humidity control. |
3. Installation and Maintenance
Single-unit Rotary Dehumidier |
Standard Rotary Dehumidifier |
Plug-and-Play: Connect to power and an exhaust hose for immediate operation; no professional installation team required. |
Engineered Installation: Requires professional design of ductwork and integration with regeneration heat sources (e.g., steam or electric heating), involving extended installation timelines. |
Simplified Maintenance: Filter replacement and rotor cleaning can be performed on-site by users. |
Modular Maintenance: Regeneration units or rotors may need disassembly for servicing, requiring system shutdowns during operations. |
4. Functionality and Performance
Single-unit Rotary Dehumidier |
Standard Rotary Dehumidifier |
Humidity Control Range: Typically covers a dew point of -20°C to RH 30%, suitable for standard low-humidity requirements. |
Deep Dehumidification Capability: Achieves a dew point below -50°C, meeting ultra-low humidity requirements (e.g., semiconductor packaging, lithium battery electrode drying). |
Moderate Airflow Capacity: Generally 100–5,000 m³/h, suited for localized areas. |
High Airflow Capacity: Single-unit airflow up to 10,000–50,000 m³/h, covering entire workshops or production lines. |
Lower Energy Efficiency: Higher energy consumption for regeneration heating, ideal for short-term or intermittent operation. |
Energy-Saving Design: Some models recover regeneration heat or integrate with waste heat systems, significantly reducing long-term operational costs. |
5. Cost Comparison
Single-unit Rotary Dehumidier |
Standard Rotary Dehumidifier |
Lower Initial Cost: Equipment pricing ranges from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands RMB, ideal for budget-constrained projects. |
Higher Initial Investment: Requires customized engineering and installation, with costs potentially exceeding 1 million RMB (or ~$150,000). |
Higher Operating Costs: Energy consumption primarily from electric regeneration heating, best suited for short-term or small-scale applications. |
Long-Term Cost Efficiency: Heat recovery or industrial waste heat utilization significantly reduces operational expenses (typically 30–50% lower than standalone units). |
Summary: How to Choose?
Choose Single-unit Rotary Units When:
Space: Small to medium areas (e.g., labs, compact warehouses)
Usage: Temporary needs or budget constraints
Installation: Prioritize plug-and-play convenience
Choose Standard Units When:
Scale: Large industrial production lines
Humidity: Ultra-low humidity requirements (dew point < -40°C)
Operation: Long-term stability or customized integration (e.g., pharmaceuticals, lithium batteries, precision manufacturing)
Who we are
Ranking among China's Top 5 air humidity brands with products exported to over 50 countries. The 50,000㎡ modern factory boasts full production capabilities, supported by a professional team of 258 experts and 3 advanced testing laboratories to ensure quality, efficiency, and on-time delivery. We offer flexible one-stop services, including OEM, ODM, JDM, and more.
Our international brand, LuftGlück (German for "Joy of Air"), specializes in providing tailored humidity and temperature management solutions for key sectors such as agriculture (including medical cannabis), construction environments, food processing, and high-tech industries. With core strengths in powerful dehumidification, energy efficiency, and ultra-quiet operation, our products are certified by 3C, CQC, CE, GS, and ISO9001, helping global clients reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and achieve sustainable development.


📞Contact Us:
Email: [email protected]
LuftGlück — Joy of Air. Made in China. Trusted Worldwide.










